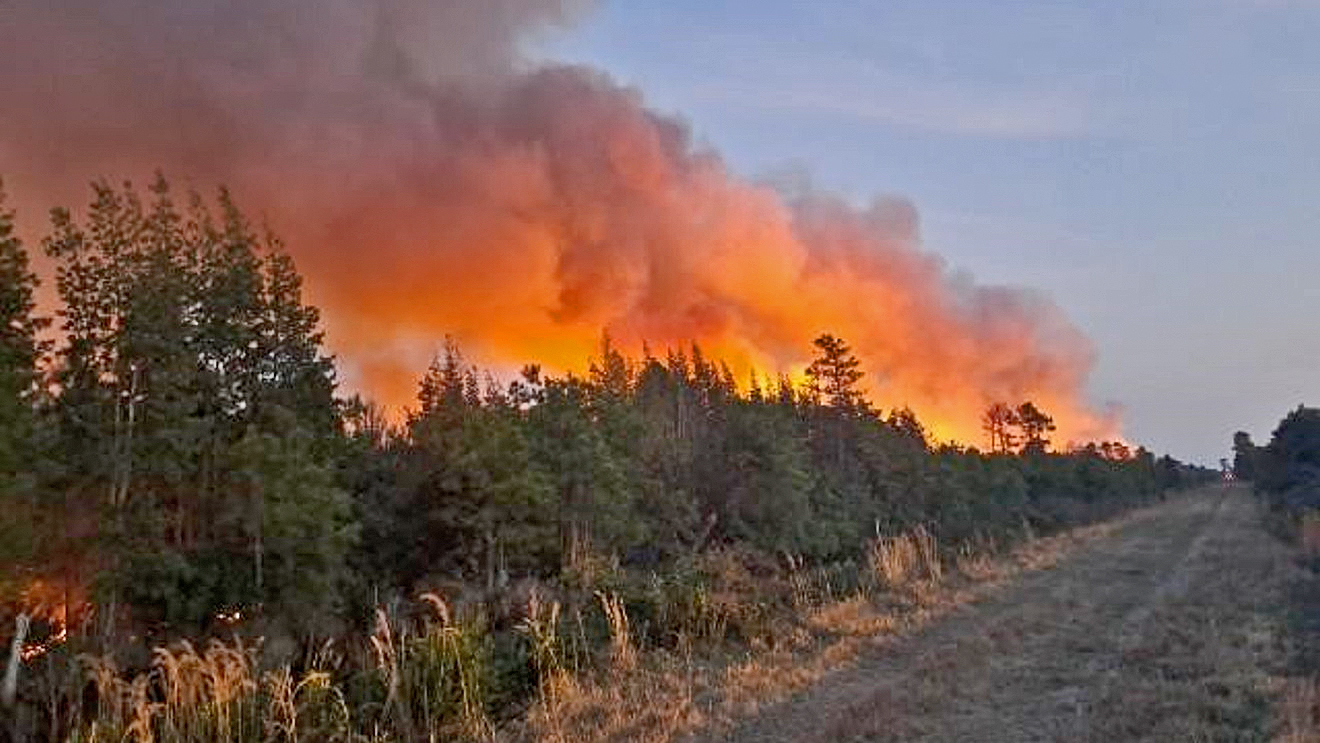
Wildfires in North Carolina are becoming increasingly common and pose a significant threat to both the environment and human life. The rise in wildfire occurrences has raised concerns about climate change, forest management, and emergency preparedness. Understanding the causes, effects, and preventive measures of wildfires is crucial for residents and policymakers alike.
North Carolina's unique geography and climate make it susceptible to wildfires, especially during dry seasons. The state's vast forested areas provide ample fuel for fires, which can quickly escalate into catastrophic events. This article explores the factors contributing to wildfires in North Carolina, their impact on ecosystems, and strategies to mitigate these disasters.
By delving into the science behind wildfires, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge needed to protect themselves and their communities. Whether you're a homeowner, environmentalist, or policymaker, this guide will provide valuable insights into the challenges posed by wildfires and the steps necessary to address them.
Read also:All About Dobby The Loyal Houseelf Who Stole Our Hearts
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Wildfires in North Carolina
- Causes of Wildfires in North Carolina
- Effects of Wildfires on the Environment
- Impact on Human Life and Property
- Wildfire Management Strategies
- Prevention Measures for Residents
- Emergency Preparedness and Response
- The Role of Climate Change
- Key Statistics and Data
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Wildfires in North Carolina
Understanding the Phenomenon
North Carolina's wildfires are a growing concern, with both natural and human-induced factors contributing to their frequency and intensity. The state's diverse ecosystems, ranging from coastal plains to mountainous regions, create varying conditions that influence wildfire behavior. Understanding these dynamics is essential for effective wildfire management.
Wildfires in North Carolina are primarily caused by a combination of prolonged droughts, high temperatures, and human activities such as campfires, fireworks, and discarded cigarettes. These factors, coupled with the state's dense forests, create an environment conducive to rapid fire spread. As a result, wildfires have become a recurring issue in North Carolina, requiring proactive measures to minimize their impact.
Causes of Wildfires in North Carolina
Natural Causes
Natural causes play a significant role in the occurrence of wildfires in North Carolina. Lightning strikes are one of the primary natural triggers, especially during thunderstorms. Additionally, drought conditions exacerbate the risk by drying out vegetation, making it more flammable. These natural factors highlight the importance of monitoring weather patterns and implementing preventive measures during high-risk periods.
Human-Induced Causes
Human activities are responsible for a substantial portion of wildfires in North Carolina. Campfires left unattended, improper disposal of cigarettes, and arson are among the leading causes. Furthermore, agricultural practices such as controlled burns can sometimes spiral out of control, leading to unintended consequences. Educating the public about fire safety and enforcing regulations can significantly reduce human-induced wildfires.
Effects of Wildfires on the Environment
Impact on Ecosystems
Wildfires have profound effects on North Carolina's ecosystems. They can lead to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and soil degradation. The intense heat from fires can kill plants and animals, disrupt food chains, and alter the landscape. However, some ecosystems, such as longleaf pine forests, have evolved to depend on periodic fires for regeneration. Balancing wildfire management with ecological needs is a complex challenge.
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term effects of wildfires extend beyond immediate damage. Soil erosion, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions are some of the lasting impacts. These consequences can affect local communities and the environment for years, necessitating comprehensive restoration efforts. Restoring affected areas requires collaboration between government agencies, environmental organizations, and local communities.
Read also:Layla Kiffin The Life And Influence Of A Football Coachs Wife
Impact on Human Life and Property
Risk to Communities
Wildfires pose a direct threat to human life and property in North Carolina. Residential areas located near forests, known as the wildland-urban interface, are particularly vulnerable. Evacuations, property damage, and loss of life are potential outcomes of severe wildfires. Strengthening building codes, creating defensible spaces, and improving emergency communication systems are critical for protecting communities.
Economic Implications
The economic impact of wildfires in North Carolina is significant. Firefighting efforts, property damage, and loss of tourism revenue can strain local economies. Additionally, the cost of post-fire restoration and infrastructure repair adds to the financial burden. Investing in preventive measures and disaster preparedness can help mitigate these economic losses.
Wildfire Management Strategies
Controlled Burns
Controlled burns, also known as prescribed fires, are a vital tool in wildfire management. By intentionally setting small fires under controlled conditions, forest managers can reduce the buildup of flammable materials and promote ecosystem health. This proactive approach helps prevent larger, uncontrolled wildfires from occurring. However, careful planning and execution are essential to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Forest Management Practices
Effective forest management practices are crucial for reducing wildfire risks. Thinning overgrown forests, removing dead vegetation, and promoting diverse plant species can create healthier ecosystems less prone to fire. Collaboration between government agencies, landowners, and conservation groups is necessary to implement these practices on a large scale.
Prevention Measures for Residents
Creating Defensible Spaces
Residents in wildfire-prone areas can take steps to protect their homes by creating defensible spaces. This involves clearing flammable materials, such as dried leaves and branches, from around the property. Planting fire-resistant vegetation and maintaining a well-watered lawn can further reduce the risk of fire spreading to homes.
Fire Safety Education
Education is a powerful tool in wildfire prevention. Programs that teach fire safety to children and adults can raise awareness about the dangers of wildfires and promote responsible behavior. Community workshops, school programs, and public campaigns can help disseminate this vital information.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Developing Emergency Plans
Preparing for wildfires involves developing comprehensive emergency plans. Residents should create evacuation plans, assemble emergency kits, and stay informed about local fire conditions. Local governments and emergency services play a crucial role in coordinating response efforts and ensuring public safety during wildfire events.
Improving Communication Systems
Effective communication is essential during wildfire emergencies. Advanced warning systems, such as text alerts and sirens, can notify residents of impending dangers. Ensuring reliable communication channels and educating the public on how to respond to alerts can save lives during wildfire events.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate Change and Wildfire Trends
Climate change is a significant factor influencing wildfire trends in North Carolina. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events contribute to the likelihood and intensity of wildfires. Addressing climate change through global and local initiatives is crucial for reducing wildfire risks in the long term.
Adapting to Changing Conditions
Adapting to the changing climate requires innovative approaches to wildfire management. Developing climate-resilient infrastructure, enhancing early warning systems, and investing in research and technology can help communities better prepare for future wildfires. Collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential for implementing effective adaptation strategies.
Key Statistics and Data
Wildfire Occurrences in North Carolina
According to the North Carolina Forest Service, the state experiences an average of 4,000 wildfires annually, burning approximately 18,000 acres of land. These numbers highlight the scale of the problem and emphasize the need for continued vigilance and action. Monitoring these statistics helps inform policy decisions and resource allocation for wildfire management.
Global Context
Globally, wildfires are becoming more frequent and severe due to climate change and human activities. The World Resources Institute reports that fire seasons are lengthening in many regions, including North Carolina. Understanding the global context of wildfires provides valuable insights into best practices and potential solutions that can be applied locally.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Wildfires in North Carolina present a significant challenge that requires collective action from all stakeholders. By understanding the causes, effects, and management strategies of wildfires, we can work together to minimize their impact on our environment and communities. Implementing preventive measures, enhancing emergency preparedness, and addressing climate change are critical steps in this effort.
We invite you to take action by sharing this article, participating in local wildfire prevention programs, and staying informed about fire safety. Your involvement can make a difference in protecting North Carolina's natural beauty and ensuring the safety of its residents. Together, we can build a more resilient future in the face of wildfire threats.