Blue is one of the most captivating colors in the spectrum, and understanding how it is created can enhance your artistic skills and knowledge of color theory. Whether you're an artist, a designer, or simply someone curious about the science of color, this article will provide you with in-depth insights into what two colors make blue. We will explore the principles of color mixing, delve into the world of pigments and light, and uncover fascinating facts about the color blue.
Color mixing is an essential skill for anyone working with art and design. By understanding how primary colors combine to create secondary colors, you can achieve the exact hue you desire. In this article, we will focus on the process of creating blue and explain the differences between color mixing in pigments and light. Whether you're working with paint, digital tools, or other mediums, this guide will be valuable for your creative endeavors.
As we journey through the world of colors, we will also touch upon the psychological and cultural significance of blue. This color has been revered throughout history, and its creation remains a fascinating topic for artists and scientists alike. Let's dive into the world of color mixing and discover what two colors make blue.
Read also:All About Dobby The Loyal Houseelf Who Stole Our Hearts
Table of Contents
- Understanding Color Theory
- What Two Colors Make Blue in Pigment Mixing?
- What Two Colors Make Blue in Light Mixing?
- The Role of Primary Colors in Creating Blue
- Exploring Secondary Colors
- Creating Different Shades of Blue
- The Science Behind Color Mixing
- The Use of Blue in Art and Design
- The Psychology of Blue
- Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Blue
Understanding Color Theory
Color theory is the foundation of all color-related activities, from painting to digital design. It involves understanding how colors interact with each other and how they can be combined to create new hues. At the heart of color theory are the concepts of primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. Primary colors are the building blocks of all other colors, and they cannot be created by mixing other colors. Secondary colors, on the other hand, are created by mixing two primary colors. Tertiary colors are a combination of primary and secondary colors.
In the context of "what two colors make blue," it's important to distinguish between pigment-based color mixing and light-based color mixing. Each system has its own set of primary colors, which affects the outcome of color mixing. By understanding these differences, you can achieve the desired blue hue more effectively.
Primary Colors in Color Mixing
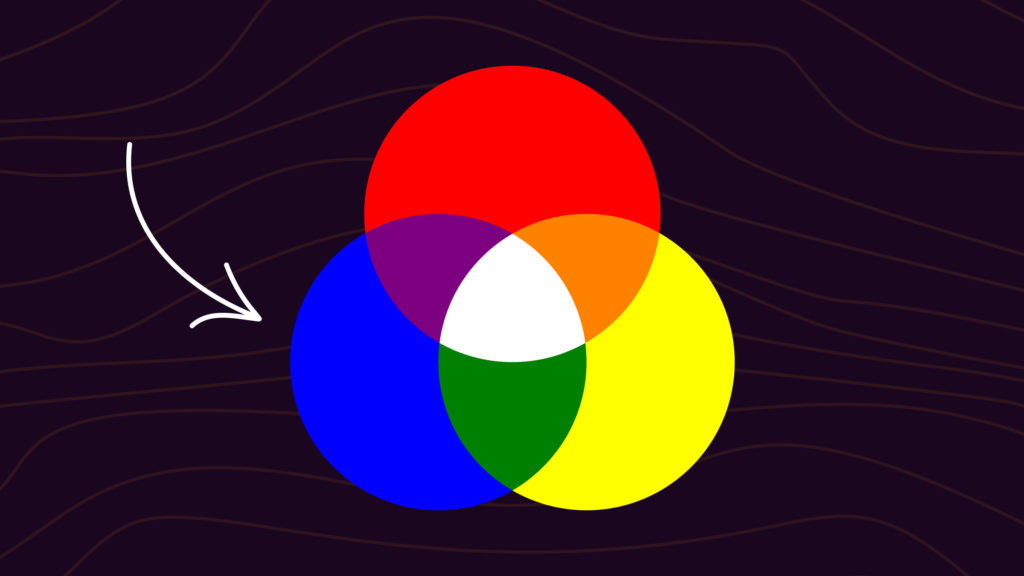
Primary colors are the foundation of color theory. In pigment-based systems, such as painting, the primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. In light-based systems, such as digital displays, the primary colors are red, green, and blue (RGB). These differences are crucial when determining what two colors make blue in different contexts.
What Two Colors Make Blue in Pigment Mixing?
In pigment-based color mixing, blue is considered a primary color. This means that blue cannot be created by mixing other colors. However, if we focus on the concept of "what two colors make blue," we can explore the opposite process—mixing blue with other colors to create new hues. For example, mixing blue with yellow creates green, while mixing blue with red creates violet.
It's worth noting that while blue cannot be created by mixing other pigments, artists often use blue as a base color to create various shades and tones. This flexibility allows for endless possibilities in art and design.
Creating Different Shades of Blue with Pigments
- Adding white to blue creates lighter shades, such as baby blue or sky blue.
- Adding black to blue creates darker shades, such as navy blue or midnight blue.
- Mixing blue with green produces teal or turquoise shades.
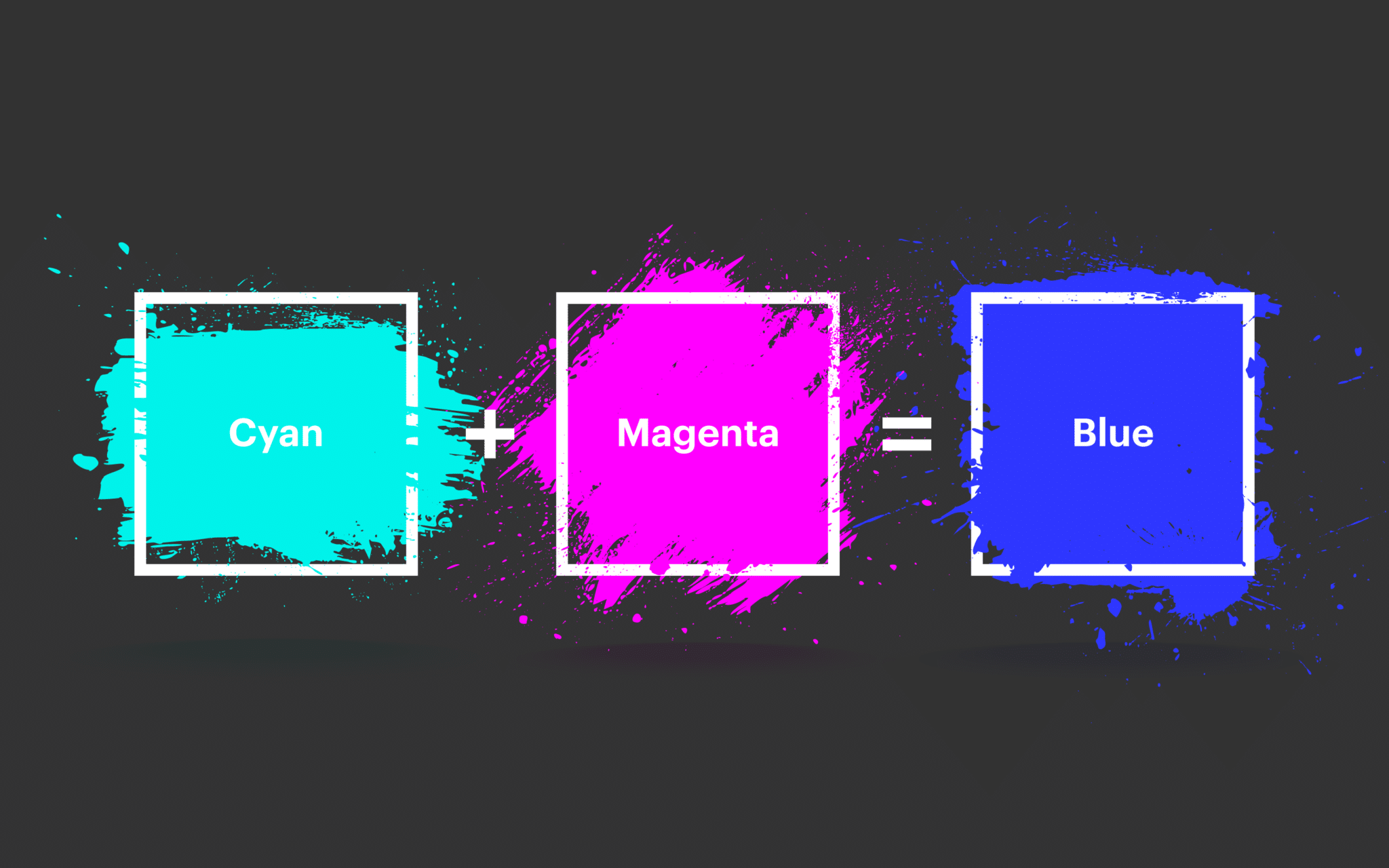
What Two Colors Make Blue in Light Mixing?
In light-based systems, such as computer screens or projectors, the primary colors are red, green, and blue (RGB). When it comes to "what two colors make blue" in this context, the answer lies in understanding how light interacts. Blue is one of the primary colors in the RGB system, so it cannot be created by mixing two other colors. However, blue light can be combined with other colors to produce secondary and tertiary colors.
Read also:What Does It Mean To Court A Lady A Timeless Tradition Of Romance
For example, mixing blue light with green light creates cyan, while mixing blue light with red light creates magenta. These combinations are essential in digital color mixing and are widely used in graphic design and video production.
Applications of Light Mixing in Technology
Light-based color mixing is the backbone of modern technology. From television screens to smartphone displays, the RGB system is used to create vibrant and realistic images. Understanding how blue interacts with other colors in this system is crucial for anyone working in digital media.
The Role of Primary Colors in Creating Blue
Primary colors play a vital role in the creation of all other colors. In pigment-based systems, blue is a primary color, meaning it cannot be created by mixing other colors. However, its role in color mixing is significant, as it serves as the foundation for creating secondary and tertiary colors. By understanding the properties of blue as a primary color, artists and designers can achieve more accurate and vibrant results in their work.
In light-based systems, blue is also a primary color. Its interaction with other primary colors, such as red and green, enables the creation of a wide range of hues. This versatility makes blue an essential component of modern technology and digital media.
Exploring Secondary Colors
Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors. In pigment-based systems, the secondary colors are green, orange, and violet. In light-based systems, the secondary colors are cyan, magenta, and yellow. Understanding how these colors are formed can help you achieve the desired blue hue in your projects.
For example, if you want to create a greenish-blue shade, you can mix blue with green. Similarly, if you want a purplish-blue shade, you can mix blue with red. The possibilities are endless, and the key lies in understanding the principles of color mixing.
Creating Custom Blue Shades
- Mixing blue with green produces teal or turquoise shades.
- Mixing blue with red produces violet or indigo shades.
- Mixing blue with yellow creates greenish-blue shades.
Creating Different Shades of Blue
Blue is a versatile color that can be manipulated to create a wide range of shades and tones. By adding white, black, or other colors, you can achieve different effects and moods in your artwork. For example, lighter shades of blue, such as baby blue or powder blue, evoke a sense of calm and serenity. Darker shades, such as navy blue or cobalt blue, convey strength and authority.
Understanding how to create these variations is essential for artists and designers who want to convey specific emotions or messages through their work. By experimenting with different color combinations, you can achieve the perfect blue hue for your project.
Psychological Effects of Different Blue Shades
Research has shown that different shades of blue can evoke different emotional responses. Light blue is often associated with calmness and tranquility, making it a popular choice for bedrooms and relaxation spaces. Dark blue, on the other hand, is linked to professionalism and trust, making it ideal for corporate environments. By understanding these psychological effects, you can use blue more effectively in your designs.
The Science Behind Color Mixing
The science of color mixing involves understanding how light and pigments interact to create different colors. In pigment-based systems, colors are created by subtracting certain wavelengths of light. For example, when you mix blue and yellow paint, the resulting green color is created by reflecting green light and absorbing other wavelengths. In light-based systems, colors are created by adding different wavelengths of light. This additive process is what enables the creation of vibrant and realistic images on digital screens.
By studying the science of color mixing, you can gain a deeper understanding of how colors work and how they can be manipulated to achieve specific effects. This knowledge is invaluable for anyone working in art, design, or technology.
The Use of Blue in Art and Design
Blue has been a popular color in art and design for centuries. From the iconic blue-and-white porcelain of ancient China to the modernist paintings of Yves Klein, blue has played a significant role in the world of art. Artists and designers often use blue to convey emotions such as calmness, trust, and serenity. Its versatility makes it a favorite among creatives working in various mediums.
In addition to its aesthetic appeal, blue also has practical applications in design. For example, it is often used in corporate branding to convey professionalism and reliability. Understanding how to use blue effectively can enhance the impact of your designs and make them more memorable.
Famous Blue Artworks
- Yves Klein's "International Klein Blue" series
- Vincent van Gogh's "Starry Night"
- Monet's "Water Lilies" series
The Psychology of Blue
Blue is often associated with positive emotions such as calmness, trust, and serenity. It is also linked to negative emotions such as sadness and melancholy, as seen in the phrase "feeling blue." The psychological effects of blue are influenced by cultural and personal factors, making it a complex and fascinating color to study.
Research has shown that blue can have a calming effect on the mind and body, making it a popular choice for spaces designed for relaxation and meditation. Its association with trust and reliability also makes it a favorite in corporate branding and marketing.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Blue
In conclusion, understanding "what two colors make blue" involves exploring the principles of color theory and the differences between pigment-based and light-based color mixing. Blue is a primary color in both systems, meaning it cannot be created by mixing other colors. However, its role in color mixing is significant, as it serves as the foundation for creating secondary and tertiary colors.
By mastering the art of blue, you can enhance your artistic skills and create more impactful designs. Whether you're working with pigments, light, or digital tools, the principles of color mixing remain the same. We encourage you to experiment with different color combinations and share your results in the comments below. Don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world of color and design.